An AI Agent is a software program that can autonomously perceive its environment, process information, make decisions, and take actions to achieve specific goals — often without constant human intervention.

It uses AI models, rules, and sometimes memory to perform tasks like answering questions, automating workflows, or even interacting with other systems.
Think of it as a digital assistant that not only follows instructions but can plan, adapt, and learn to improve over time.
Examples:
- Customer service bots answering support queries
- Automated research assistants gathering and summarising data
- Business process automation agents handle repetitive tasks
How to Create an AI Agent
1. Define the Purpose
- What will your AI agent do? (e.g., customer support, lead generation, scheduling, automation)
- Identify user needs and success metrics.
2. Choose the Platform or Framework
- No-Code / Low-Code Tools: ChatGPT, Zapier, Botpress, ManyChat
- Developer Frameworks: LangChain, AutoGen, Microsoft Semantic Kernel, Rasa
- Integration Platforms: OpenAI API, Hugging Face models, Google Vertex AI
3. Design the Workflow
- Define triggers (what starts the agent’s action)
- Define actions (what tasks it performs)
- Define decision-making logic (how it chooses what to do next)
4. Train or Configure the Agent
- Use pre-trained AI models or fine-tune with your own data
- Provide examples (prompts, scripts, Q&A sets)
- Add knowledge bases for accuracy
5. Integrate with Data & Tools
- Connect to CRMs, email systems, databases, APIs
- Allow the AI agent to read, write, and update relevant information
6. Test and Optimise
- Run simulations with real use cases
- Monitor performance & improve prompts or training data
Benefits of AI Agents
- Automation of Repetitive Tasks
- Saves time by handling routine work without human effort.
- 24/7 Availability
- Works around the clock, ensuring faster response times.
- Cost Efficiency
- Reduces the need for large teams for simple, repetitive operations.
- Scalability
- Can handle multiple tasks and thousands of requests simultaneously.
- Data-Driven Decisions
- Uses AI analytics to make accurate, quick, and consistent decisions.
- Personalization
- Learns from user interactions to provide more relevant responses over time.
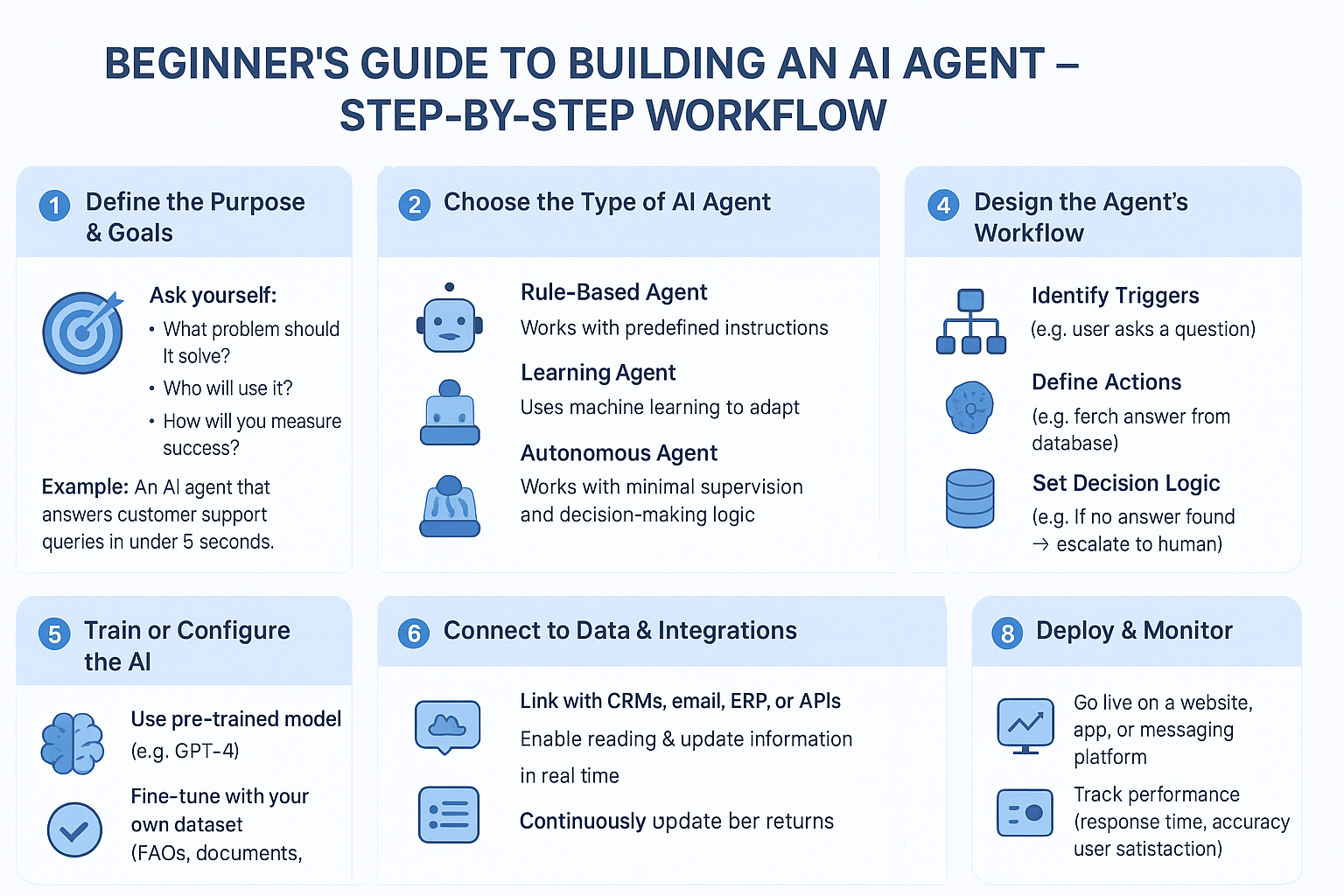
Beginner’s Guide to Building an AI Agent – Step-by-Step Workflow
1. Define the Purpose & Goals
🎯 Ask yourself:
- What problem should it solve?
- Who will use it?
- How will you measure success?
📌 Example: “An AI agent that answers customer support queries in under 5 seconds.”
2. Choose the Type of AI Agent
- Rule-Based Agent → Works with predefined instructions
- Learning Agent → Uses machine learning to adapt
- Autonomous Agent → Works with minimal supervision and decision-making logic
3. Select Your Tools & Platforms
- No-Code: ChatGPT, Botpress, Zapier, ManyChat
- Developer Frameworks: LangChain, AutoGen, Rasa, Microsoft Semantic Kernel
- APIs: OpenAI API, Hugging Face, Google Vertex AI
4. Design the Agent’s Workflow
🛠 Steps:
- Identify Triggers (e.g., user asks a question)
- Define Actions (e.g., fetch answer from database)
- Set Decision Logic (e.g., if no answer found → escalate to human)
5. Train or Configure the AI
- Use pre-trained models (e.g., GPT-4)
- Fine-tune with your own dataset (FAQs, documents, past chat logs)
- Give clear prompts and examples for accurate responses
6. Connect to Data & Integrations
- Link with CRMs, email, ERP, or APIs
- Enable reading & updating info in real time
7. Test the Agent
- Run simulations with real-world scenarios
- Identify errors, refine prompts, improve logic
8. Deploy & Monitor
- Go live on website, app, or messaging platform
- Track performance (response time, accuracy, user satisfaction)
- Continuously update for better results
Benefits You’ll See Quickly
✅ Handles repetitive work automatically
✅ Available 24/7
✅ Reduces operational costs
✅ Scales with your business needs
✅ Learns and improves over time